

#COPAY VS DEDUCTIBLE DOWNLOAD#
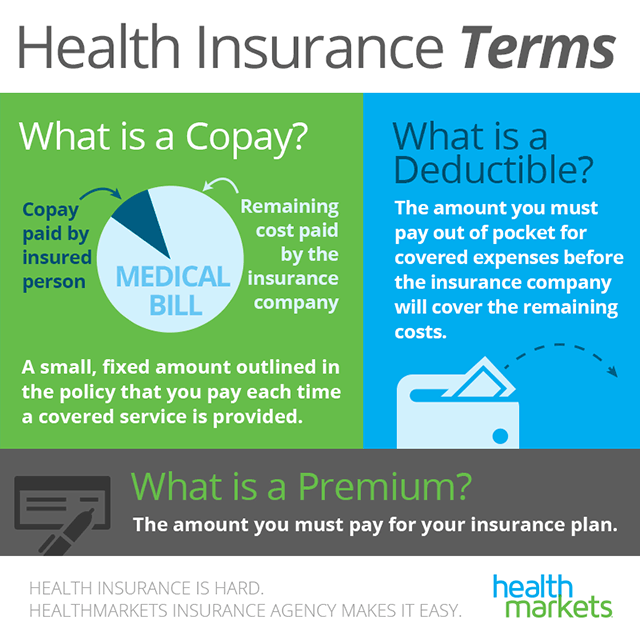
Download the e-book: 8 Proven Strategies for Growing your Revenue Cycle Management Company What is Copay?Ī copay is a set amount you pay upfront for your healthcare services, whether doctor visits or prescription drugs. In this article, we will talk about co-pay, coinsurance, and deductibles, the difference between them, and how they can vary so that you can estimate your medical costs.ĭiscover how leading revenue cycle management companies achieve comprehensive growth goals that go beyond costs and bottom lines.

It is important to understand the differences between these terms. Insurance companies typically impose cost sharing in three ways: co-payments, coinsurance, and deductibles. Cost sharing is when your insurance company requires you to pay a portion of the cost of a medical treatment, such as a lab test or an outpatient operation. In health insurance, it is common for expenses to add up fast. By understanding the differences between copay and coinsurance, you can make more informed decisions about your healthcare costs and choose the best plan for your needs. Copays are typically used for more routine services, while coinsurance is more commonly used for larger, more expensive services such as surgery or hospitalization. For example, if your coinsurance is 20% and the total cost of a service is $100, you would pay $20 and your insurance would cover the remaining $80. On the other hand, coinsurance is a percentage of the total cost of a service that you’re responsible for paying. A copay is a fixed amount that you pay out of pocket for a specific service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription medication. You may have to pay the $100 difference.When it comes to healthcare services, copays and coinsurance are two common types of cost-sharing.Your plan covers a maximum of $200 for an X-ray.
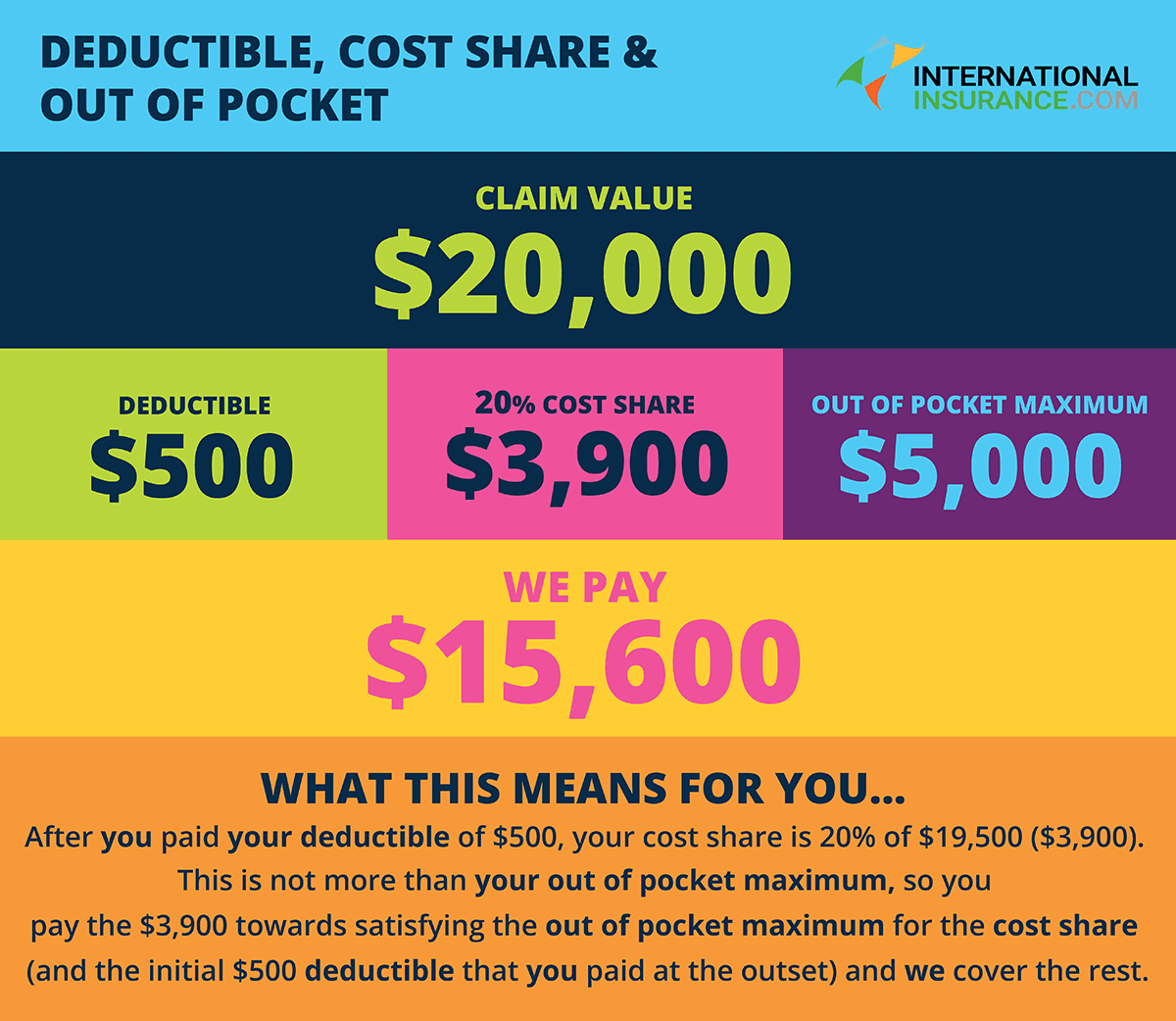
Let's say your doctor charges more for an X-ray. These limits help keep rates fair and reasonable, which helps lower costs for all members. Your plan covers up to a certain amount for tests, procedures and medical services. Your out-of-pocket cost, or coinsurance, is $40.What you pay to see your doctor depends on your coinsurance, which in our example, is 20%. You've met your annual $5,000 deductible so your plan now pays for benefits. You bruise your hip in a fall and you need an X-ray. Example #2: Coinsurance After You've Met Your Deductible A plan is good for one year.Īt the start of each year, your deductible and coinsurance resets for the next plan year and the $5,000 deductible and 20% coinsurance will start again. When the amount of coinsurance you've paid reaches $1,000, you will have paid $6,000 and at that point the plan covers 100% until your "plan year" ends.After that, your plan covers 80% of the costs, and you pay the other 20%.You must pay the first $5,000 of your medical costs.Example #1: Deductibles, Coinsurance and Out-of-Pocket Here are a few examples of how deductibles, coinsurance and maximum limits work together. Once you understand the different parts of your health insurance costs you’ll want to know how these work together and what your out-of-pocket costs may be.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
